Gaskets
Gasket Solutions – Seals & Gaskets for Every Application
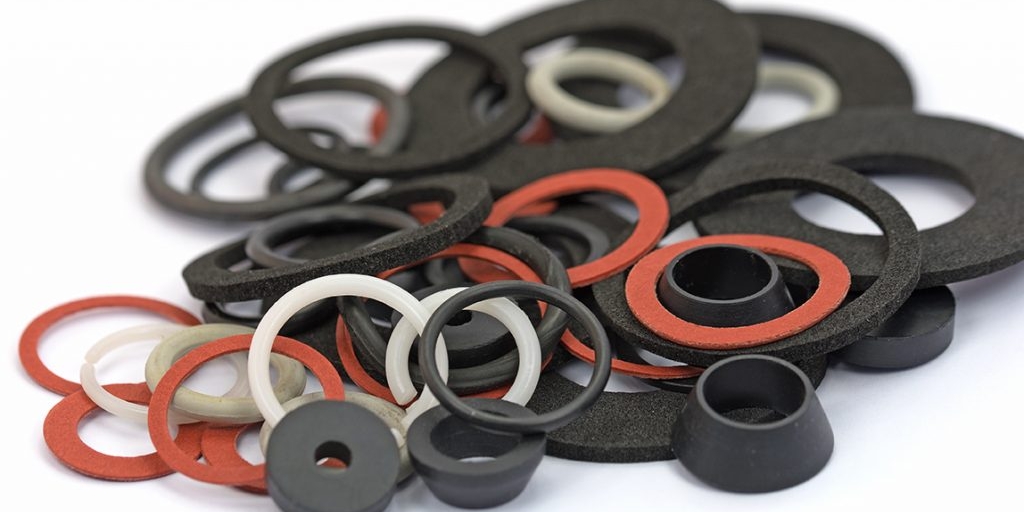

Gaskets and seals are components used in various industries to prevent the leakage of fluids or gases between two joined surfaces. They play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of systems by creating a barrier that prevents the escape of liquids or gases and, in some cases, prevents the entry of contaminants. Here's a brief overview of each:
- Gaskets:
- Function: Gaskets are mechanical seals that fill the space between two or more mating surfaces, generally to prevent leakage from or into the joined objects while under compression.
- Materials: Gaskets can be made from a variety of materials, including rubber, metal, cork, fiberglass, or a combination of materials. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the properties required (e.g., resistance to temperature, pressure, and chemicals).
- Applications: Gaskets are commonly used in the automotive industry (in engines and exhaust systems), plumbing, pipelines, and manufacturing equipment where the sealing of joints is critical.
- Seals:
- Function: Seals, like gaskets, are used to prevent the escape of fluids or gases, but they are more general in their application. Seals can be used in rotating or moving parts, such as shafts, to prevent the leakage of lubricants or to keep out contaminants.
- Types: There are various types of seals, including radial seals, axial seals, lip seals, and O-rings. Each type is designed for specific applications and operating conditions.
- Materials: Seal materials vary based on the application and may include rubber, silicone, metal, or synthetic materials.
Both gaskets and seals are essential in maintaining the functionality and efficiency of systems, machinery, and equipment by ensuring that fluids and gases are contained within the desired areas and that external elements are kept out. The choice of gaskets and seals depends on factors such as the type of fluid or gas, temperature, pressure, and the specific requirements of the application.
What Are The Different Types Of Gaskets and Seals
- Excellent resistance to weathering, UV, and ozone.
- Flexible and durable, ideal for outdoor applications.
- Good resistance to water, steam, and mild chemicals.
- Resistant to weathering and moderate oil exposure.
- Suitable for automotive, HVAC, and marine use.
- Withstands ageing and environmental stress.
- Superior resistance to oils, fuels, and petroleum-based fluids.
- Performs well in automotive and industrial environments.
- Good chemical resistance with moderate temperature stability.
- High-temperature resistance and low-temperature flexibility.
- Excellent UV and ozone stability.
- Common in the food, medical, and electrical industries.

What is a Gasket?
A gasket is a mechanical seal placed between two or more mating surfaces to prevent the leakage of liquids or gases under compression. They create a reliable barrier, ensuring joints remain airtight or watertight, while also compensating for surface irregularities.
Unlike seals, which are often used for moving parts such as shafts, gaskets are typically used in static applications, including engines, pipelines, plumbing systems, and industrial machinery.
Why Use a Gasket?
Gaskets are essential in almost every industry where joint integrity is critical. Their main purpose is to:
- Prevent the escape of fluids or gases.
- Protect against the entry of dust, dirt, or contaminants.
- Compensate for imperfections in mating surfaces.
- Reduce vibration and absorb shocks.
- Withstand extreme temperatures and pressures.
From automotive engines to chemical plants, gaskets safeguard performance, safety, and efficiency.
Benefits of Using Gaskets
Gaskets offer a wide range of benefits, depending on the materials from which they are made. Some of the most notable include:
- Leak Prevention – ensures safe operation by containing fluids and gases.
- Versatility – available in rubber, plastic, metal, cork, or foam to suit different applications.
- Durability – resistant to oils, fuels, chemicals, and temperature variations.
- Cost-Effectiveness – prevent costly leaks, breakdowns, and system failures.
- Customisation – can be tailored to suit specialist requirements in terms of shape, thickness, and material.
Advantages of Plastic Gaskets
Plastic gaskets are increasingly popular due to their lightweight and versatile properties. Key advantages include:
- Chemical Resistance – ideal for industries exposed to corrosive fluids.
- Temperature Stability – suitable for both high and low extremes.
- Electrical Insulation – PTFE and similar plastics prevent current leakage.
- Flexibility – foam plastics provide compression recovery and vibration resistance.
- Custom Fabrication – can be die-cut, CNC machined, or moulded for precision.
Specialised Plastic Gaskets
PTFE Gaskets
- Made from polytetrafluoroethylene, a highly resistant fluorocarbon.
- Provide excellent electrical insulation.
- Resistant to extreme temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
- Commonly used in electronics, chemical processing, and aerospace.


Polyethylene (EVA PE Foam) Gaskets
- Low-pressure sealing with resistance to dust and debris.
- Lightweight, elastic, and compression-resistant.
- Suitable for packaging, electronics, and HVAC.
Polyurethane Gaskets
- Abrasion-resistant with high resilience to wear and tear.
- Available in solid and sponge forms.
- Ideal for demanding environments with high friction and impact.


PVC Foam Gaskets
- Lightweight, versatile, and available in multiple grades.
- Provide gap-filling and sealing under compression.
- Can be laminated, adhesive-backed, or foil-finished for custom use.
Please contact us using the form below or by calling us on +44(0)1384 252555.